This project employs Ridge and LASSO Regression to predict college graduation rates based on a rich dataset of U.S. colleges. The project uses the College dataset from the ISLR package, which contains information about U.S. colleges and universities, including tuition fees, student demographics, and graduation rates.
By utilizing regularization techniques, this project addresses issues of multicollinearity, selects significant predictors, and provides actionable insights for improving educational outcomes.
Data Preprocessing:
Modeling Techniques:
Model Evaluation:
Visualization:
For a detailed analysis, including methodology, regularization plots, and insights, refer to the complete project report:
📄 College Graduation Rate Prediction Report
.
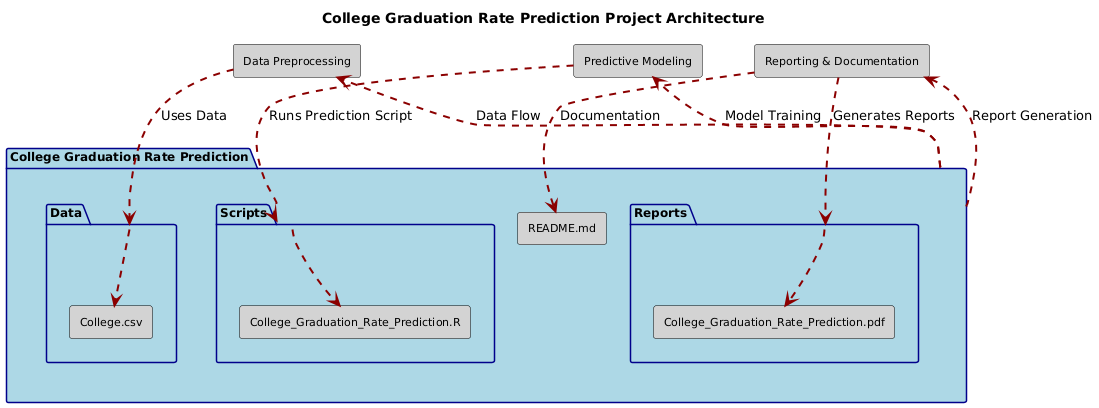
├── Data/
│ ├── College.csv
├── Scripts/
│ ├── College_Graduation_Rate_Prediction.R
├── Reports/
│ ├── College_Graduation_Rate_Prediction.pdf
├── README.md
Feel free to reach out for feedback, questions, or collaboration opportunities:
LinkedIn: Dr. Syed Faizan
Author: Syed Faizan
Master’s Student in Data Analytics and Machine Learning
| #---------------------------------------------------------# | |
| # Syed Faizan # | |
| # College Graduation Rate Prediction # | |
| # # | |
| # # | |
| # # | |
| # # | |
| #---------------------------------------------------------# | |
| # Starting with a clean environment | |
| rm(list=ls()) | |
| # Clearing the Console | |
| cat("\014") # Clears the console | |
| # Removing Scientific Notation | |
| options(scipen = 999) | |
| # Loading the packages utilized for Data cleaning and Data Analysis | |
| library(tidyverse) | |
| library(grid) | |
| library(gridExtra) | |
| library(dplyr) | |
| library(ggplot2) | |
| library(ISLR) | |
| library(caret) | |
| library(vtable) | |
| library(dlookr) | |
| library(DataExplorer) | |
| library(psych) | |
| library(pROC) | |
| library(ggcorrplot) | |
| library(glmnet) | |
| # Loading the College Dataset | |
| College <- College | |
| dim(cl) | |
| names(cl) | |
| summary(cl) | |
| View(cl) | |
| class(cl) | |
| # Since Graduation Rate is the response variable prescribed in our assignment | |
| # I wish to take a closer look at it through box plots | |
| ggplot(cl, aes(x = Private, y = Grad.Rate, fill = Private)) + | |
| geom_boxplot( alpha = 0.7, col = c("red", "blue")) + | |
| labs(title = "Graduation Rate by College Type", | |
| y = "Graduation Rate (%)", | |
| fill = "Is the College Private?") + | |
| theme(legend.position = "bottom", | |
| plot.title = element_text(hjust = 0.5), # Center the title | |
| legend.title.align = 0.5) + # Center the legend title | |
| ylim(0, 120) # Limit Y-axis to valid graduation rates | |
| # Descriptive Statistics Table for the Dataset | |
| st(cl) | |
| # RIDGE | |
| # Assignment Question 1 | |
| # Split the data into a train and test set – refer to the Feature_Selection_R.pdf | |
| # document for information on how to split a dataset. | |
| # Partition data indices for a 70% training set | |
| set.seed(123) # for reproducibility | |
| trainIndex <- createDataPartition(y = College$Private, p = 0.7, list = FALSE) | |
| train <- College[trainIndex, ] | |
| test <- College[-trainIndex, ] | |
| numPrivateColleges <- nrow(train[train$Private == "Yes", ]) | |
| numPrivateColleges | |
| numPublicColleges <- nrow(train[train$Private == "No", ]) | |
| numPublicColleges | |
| numPrivateColleges1 <- nrow(test[test$Private == "Yes", ]) | |
| numPrivateColleges1 | |
| numPublicColleges1 <- nrow(test[test$Private == "No", ]) | |
| numPublicColleges1 | |
| # Correlation and Pairs plot to facilitate analysis | |
| pairs.panels(College) | |
| cor <- cor(College[ , 2:18]) | |
| ggcorrplot(cor, lab = TRUE) | |
| # The glmnet() function takes a matrix and vector as inputs therefore | |
| # preparing the model matrix of predictors and the vector of the response variable | |
| train_x <- model.matrix(Grad.Rate ~ ., data = train)[, -1] | |
| train_y <- train$Grad.Rate | |
| test_x <- model.matrix(Grad.Rate ~ ., data = test)[, -1] | |
| test_y <- test$Grad.Rate | |
| # Assignment task 2 | |
| # Ridge Regression | |
| # Use the cv.glmnet function to estimate the lambda.min and lambda.1se values. | |
| # Compare and discuss the values. | |
| set.seed(314) | |
| cv.ridge <- cv.glmnet(x = train_x, y = train_y, alpha = 0, standardize = TRUE) #standradizing the predictors | |
| bestlam_ridge <- cv.ridge$lambda.min | |
| bestlam_1se_ridge <- cv.ridge$lambda.1se | |
| bestlam_ridge | |
| bestlam_1se_ridge | |
| # Assignment task 3 | |
| # Plot the results from the cv.glmnet function provide an interpretation. | |
| # What does this plot tell us? | |
| plot(cv.ridge) | |
| # Assignment task 4 | |
| # Fit a Ridge regression model against the training set and report on the coefficients. | |
| # Is there anything interesting? | |
| ridge.mod <- glmnet(x = train_x, y = train_y, alpha = 0, lambda = bestlam_ridge) | |
| coef.ridge <- coef(ridge.mod) | |
| dim(coef.ridge) | |
| coef.ridge | |
| # Plots to understand the model | |
| ridge.mod_for_plot <- glmnet(x = train_x, y = train_y, alpha = 0) | |
| plot(ridge.mod_for_plot, xvar = "lambda", label = TRUE, xlim = c( 0, 7)) | |
| abline(v = log(c(bestlam_ridge,bestlam_1se_ridge )), col = c("green", "purple")) | |
| log(bestlam_ridge) # 0.9826 | |
| log(bestlam_1se_ridge) # 3.02 | |
| plot(ridge.mod_for_plot, xvar = "dev", label = TRUE, xlim = c( 0, 1)) | |
| abline(v = log(c(bestlam_ridge,bestlam_1se_ridge )), col = c("green", "purple")) | |
| # Assignment task 5 | |
| # Determine the performance of the fit model against the training set | |
| # by calculating the root mean square error (RMSE) | |
| # Making predictions on the training set using the fitted Ridge model | |
| preds_t <- predict(ridge.mod, newx = train_x) | |
| # Calculating the RMSE | |
| rmse_train_ridge <- sqrt(mean((train_y - preds_t)^2)) | |
| # Assignment task 6 | |
| # Determine the performance of the fit model against the testing set | |
| # by calculating the root mean square error (RMSE) | |
| # Making predictions on the test set using the fitted Ridge model | |
| preds_test <- predict(ridge.mod, newx = test_x) | |
| # Calculating the RMSE | |
| rmse_test_ridge <- sqrt(mean((test_y - preds_test)^2)) | |
| # Is your model overfit? | |
| rmse_train_ridge | |
| rmse_test_ridge | |
| # Yes, model is slightly overfit. | |
| plot(ridge.mod, xvar = "dev", label = TRUE, type.coef = "2norm", ylim = c(0,0.23)) | |
| #LASSO | |
| # Assignment Task 7 | |
| # Use the cv.glmnet function to estimate the lambda.min and lambda.1se values. | |
| # Compare and discuss the values. | |
| # Set the seed for reproducibility | |
| set.seed(324) | |
| # Cross-validation to find the optimal lambda and lambda 1 se using LASSO | |
| cv.lasso <- cv.glmnet(x = train_x, y = train_y, alpha = 1) | |
| bestlam_lasso <- cv.lasso$lambda.min | |
| bestlam_1se_lasso <- cv.lasso$lambda.1se | |
| # Print best lambda values | |
| bestlam_lasso | |
| bestlam_1se_lasso # log of bestlam_1se_lasso is 0.494 | |
| log(bestlam_1se_lasso) | |
| # Assignment Task 8 | |
| # Plot the results from the cv.glmnet function provide an interpretation. | |
| # What does this plot tell us? | |
| plot(cv.lasso) | |
| # Examining the Log of Lambda closely | |
| plot(cv.lasso, xlim = c(-0.5, 0.5)) | |
| # Assignment Task 9 | |
| # Fit a LASSO regression model against the training set and report on the coefficients. | |
| # Do any coefficients reduce to zero? If so, which ones? | |
| # Decided to use the 1se lambda after the guidelines of Rob Tibshirani in his seminal book | |
| # In order to avoid overfitting and greater sparsity. | |
| lasso.mod <- glmnet(x = train_x, y = train_y, alpha = 1, lambda = bestlam_1se_lasso) | |
| lasso.mod | |
| # Plots to understand model | |
| lasso.mod_for_plot <- glmnet(x = train_x, y = train_y, alpha = 1) | |
| plot(lasso.mod_for_plot, xvar = "lambda", label = TRUE, xlim = c( -6.5, 1.5)) | |
| abline(v = log(c(bestlam_lasso,bestlam_1se_lasso )), col = c("blue", "red")) | |
| log(bestlam_lasso) # -4.71563 | |
| log(bestlam_1se_lasso) # 0.4942591 | |
| plot(lasso.mod_for_plot, xvar = "dev", label = TRUE, xlim = c( 0, 0.5)) | |
| abline(v = log(c(bestlam_lasso,bestlam_1se_lasso )), col = c("blue", "red")) | |
| # limiting xlim to | |
| # between the min and 1 se of cv values of lambda | |
| # Extract the coefficients from the LASSO model | |
| coef.lasso <- coef(lasso.mod) | |
| # Display the dimensions of the coefficient matrix | |
| dim(coef.lasso) | |
| # Print the coefficients | |
| coef.lasso | |
| # Assignment task 10 | |
| # Determine the performance of the fit model against the training set | |
| # by calculating the root mean square error (RMSE) | |
| # Making predictions on the training set using the fitted LASSO model | |
| preds_tl <- predict(lasso.mod, newx = train_x) | |
| # Calculating the RMSE | |
| rmse_train_lasso <- sqrt(mean((train_y - preds_tl)^2)) | |
| # Assignment task 11 | |
| # Determine the performance of the fit model against the testing set | |
| # by calculating the root mean square error (RMSE) | |
| # Making predictions on the test set using the fitted LASSO model | |
| preds_testl <- predict(lasso.mod, newx = test_x) | |
| # Calculating the RMSE | |
| rmse_test_lasso <- sqrt(mean((test_y - preds_testl)^2)) | |
| # Output RMSE results to check for overfitting | |
| print(paste("Training RMSE with LASSO:", rmse_train_lasso)) | |
| print(paste("Test RMSE with LASSO:", rmse_test_lasso)) | |
| # Further refining Lasso model after examining the plot | |
| lasso.mod2 <- glmnet(x = train_x, y = train_y, alpha = 1, lambda = exp(-0.5)) | |
| lasso.mod2 | |
| coef(lasso.mod2) | |
| # Making predictions on the training set using the fitted LASSO model | |
| preds_tl2 <- predict(lasso.mod2, newx = train_x) | |
| # Calculating the RMSE | |
| rmse_train_lasso2 <- sqrt(mean((train_y - preds_tl2)^2)) | |
| # Determine the performance of the fit model against the testing set | |
| # by calculating the root mean square error (RMSE) | |
| # Making predictions on the test set using the fitted LASSO model | |
| preds_testl2 <- predict(lasso.mod2, newx = test_x) | |
| # Calculating the RMSE | |
| rmse_test_lasso2 <- sqrt(mean((test_y - preds_testl2)^2)) | |
| # Output RMSE results to check for overfitting | |
| print(paste("Training RMSE with LASSO:", rmse_train_lasso2)) | |
| print(paste("Test RMSE with LASSO:", rmse_test_lasso2)) | |
| # Variable importance | |
| varImp(lasso.mod2, scale = F,lambda = exp(-0.5) ) | |
| # Comparison | |
| # Assignment Task 12 | |
| # Which model performed better and why? Is that what you expected? | |
| model_list <- list(ridge.mod, lasso.mod, lasso.mod2) | |
| model_list | |
| # Refer to the Intermediate_Analytics_Feature_Selection_R.pdf document for how to perform stepwise selection and then fit a model. | |
| # Did this model perform better or as well as Ridge regression or LASSO? Which method do you prefer and why? | |
| # Fit model based on stepwise selection | |
| stepwise_model <- step(lm(Grad.Rate ~ ., data = train), direction = "both") | |
| # Make predictions on the test set | |
| stepwise_preds <- predict(stepwise_model, newdata = test) | |
| # Calculate RMSE for the test set | |
| stepwise_rmse <- sqrt(mean((test$Grad.Rate - stepwise_preds)^2)) | |
| stepwise_rmse | |
| # Compare models | |
| comparison <- data.frame( | |
| Model = c("Ridge","LASSO 2", "Stepwise", "LASSO 1"), | |
| RMSE = c(rmse_test_ridge,rmse_test_lasso2,stepwise_rmse, rmse_test_lasso ) | |
| ) | |
| comparison <- comparison %>% | |
| arrange(RMSE) | |
| comparison | |
| best.model <- comparison[ 1, ] | |
| best.model # Ridge Regression | |
| # END OF PROJECT |



© 2025 Syed Faizan. All Rights Reserved.