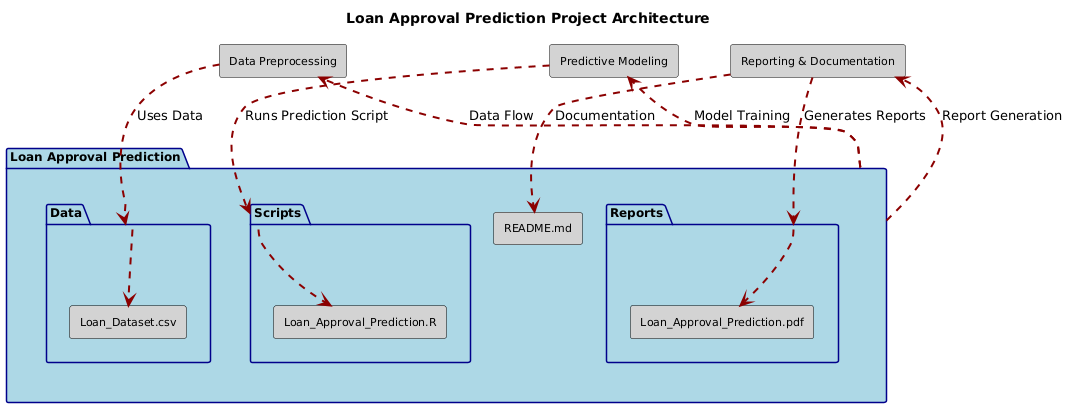
This project focuses on predicting loan approval using a variety of machine learning models, including Logistic Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forests, and Gradient Boosting. The analysis is based on the Loan Dataset, comprising 614 records and 13 attributes related to loan applicants. The aim is to automate and optimize the loan approval process while maintaining high accuracy and consistency.
Data Preprocessing:
Modeling Techniques:
Evaluation Metrics:
Insights and Business Impact:
For a detailed analysis, including methodology, visualizations, and results, refer to the complete project report:
📄 Loan Approval Prediction Report
.
├── Data/
│ ├── Loan_Dataset.csv
├── Scripts/
│ ├── Loan_Approval_Prediction.R
├── Reports/
│ ├── Loan_Approval_Prediction.pdf
├── README.md
Feel free to reach out for feedback, questions, or collaboration opportunities:
LinkedIn: Dr. Syed Faizan
Author: Syed Faizan
Master’s Student in Data Analytics and Machine Learning
| #---------------------------------------------------------# | |
| #Loan Approval Prediction - Syed Faizan # | |
| # # | |
| #---------------------------------------------------------# | |
| # Starting with a clean environment | |
| rm(list=ls()) | |
| # Clearing the Console | |
| cat("\014") # Clears the console | |
| # Clearing scientific notation | |
| options(scipen = 999) | |
| # Loading the necessary packages for Data cleaning and Analysis | |
| # Installing libraries if not already installed | |
| # Loading libraries | |
| library(rpart, quietly = TRUE) | |
| library(caret, quietly = TRUE) | |
| library(randomForest, quietly = TRUE) | |
| library(ipred, quietly = TRUE) | |
| library(xgboost, quietly = TRUE) | |
| library(MASS, quietly = TRUE) | |
| library(rpart.plot, quietly = TRUE) | |
| library(rattle) | |
| library(readr) | |
| # Reading the data set as a data frame | |
| loanfinal <- read_csv("Loanfinal.csv") | |
| # Checking the structure of the data | |
| str(loanfinal) | |
| # Checking for missing values | |
| sum(is.na(loanfinal)) | |
| library(DataExplorer) | |
| plot_missing(loanfinal) | |
| # Imputing missing values using KNN | |
| # Load the VIM library | |
| library(VIM) | |
| # Perform k-NN imputation | |
| loanfinal_imputed <- kNN(loanfinal, k = 5) # k = 5 is a commonly used default | |
| # Checking the structure after imputation | |
| str(loanfinal_imputed) | |
| # The kNN function adds additional columns with the suffix "_imp" to indicate | |
| # which values were imputed. If you want to remove these indicators: | |
| loanfinal_imputed <- loanfinal_imputed[, !grepl("_imp", names(loanfinal_imputed))] | |
| sum(is.na(loanfinal_imputed)) | |
| loanfinal <- loanfinal_imputed | |
| # Dropping any unnecessary variables if applicable | |
| # e.g., loanfinal$some_column <- NULL | |
| # Analyzing the 'Loan_Status' variable | |
| table(loanfinal$Loan_Status) | |
| # Feature Engineering | |
| hist(loanfinal$ApplicantIncome, | |
| xlab = 'Applicant Income', | |
| ylab= 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Applicant Income', | |
| col = 'red') | |
| # Try square root transformation | |
| AppIncomesqrt <- sqrt(loanfinal$ApplicantIncome) | |
| hist(AppIncomesqrt, | |
| xlab = 'Square Root of Applicant Income', | |
| ylab= 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Applicant Income', | |
| col = 'blue') | |
| # Apply transformation | |
| loanfinal$ApplicantIncome <- sqrt(loanfinal$ApplicantIncome) | |
| #Apply similar transformations to other numeric variables after visualization | |
| # Coapplicant Income | |
| hist(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome, | |
| xlab = 'Coapplicant Income', | |
| ylab = 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Coapplicant Income', | |
| col = 'green', | |
| breaks = 50) | |
| # Trying square root transformation | |
| CoappIncomesqrt <- sqrt(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome) | |
| hist(CoappIncomesqrt, | |
| xlab = 'Square Root of Coapplicant Income', | |
| ylab = 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Square Root of Coapplicant Income', | |
| col = 'purple', | |
| breaks = 50) | |
| # Add a small constant to avoid log(0) | |
| CoappIncome_log <- log(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome + 1) | |
| # Plot the histogram after log transformation | |
| hist(CoappIncome_log, | |
| xlab = 'Log of Coapplicant Income', | |
| ylab = 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Log Transformed Coapplicant Income', | |
| col = 'lightblue', | |
| breaks = 50) | |
| sum(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome == 0) #There are 273 zeros in this column | |
| # I have decided to thus turn it into categorical column with 'yes' or 'no' as levels | |
| loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome <- ifelse(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome != 0, 'yes', 'no') | |
| table(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome) # 273 No and 341 Yes | |
| loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome <- factor(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome, levels = c('yes','no')) #factorize co-applicant income | |
| # confirm factorization and the levels | |
| class(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome) | |
| levels(loanfinal$CoapplicantIncome) | |
| # Convert all character columns to factors | |
| loanfinal[sapply(loanfinal, is.character)] <- lapply(loanfinal[sapply(loanfinal, is.character)], as.factor) | |
| str(loanfinal) | |
| # visualization | |
| library(ggplot2) | |
| ggplot(loanfinal, aes(x = CoapplicantIncome, fill = factor(Loan_Status))) + | |
| geom_histogram(color = "red", alpha = 0.7, stat="count", bins = 30) + | |
| scale_fill_manual(values = c("Y" = "blue", "N" = "orange")) + # Using actual levels from Loan_Status | |
| labs(x = "Coapplicant Income", fill = "Loan Status") + | |
| ggtitle("Coapplicant Income by Loan Status") + | |
| theme_bw() | |
| # LoanAmount | |
| hist(loanfinal$LoanAmount, | |
| xlab = 'Loan Amount', | |
| ylab = 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Loan Amount', | |
| col = 'orange', | |
| breaks = 50) | |
| # Try square root transformation | |
| LoanAmountsqrt <- sqrt(loanfinal$LoanAmount) | |
| hist(LoanAmountsqrt, | |
| xlab = 'Square Root of Loan Amount', | |
| ylab = 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Square Root of Loan Amount', | |
| col = 'cyan', | |
| breaks = 50) | |
| # Apply transformation | |
| loanfinal$LoanAmount <- sqrt(loanfinal$LoanAmount) | |
| # Loan_Amount_Term | |
| hist(loanfinal$Loan_Amount_Term, | |
| xlab = 'Loan Amount Term', | |
| ylab = 'Frequency', | |
| main = 'Histogram of Loan Amount Term', | |
| col = 'pink', | |
| breaks = 50) | |
| # Since distribution appears to be discrete no transformation is contemplated | |
| # Data splicing | |
| set.seed(12345) | |
| train <- sample(1:nrow(loanfinal), size = ceiling(0.80 * nrow(loanfinal)), replace = FALSE) | |
| loan_train <- loanfinal[train, ] | |
| loan_test <- loanfinal[-train, ] | |
| loan_test$Loan_Status <- factor(loan_test$Loan_Status, levels = c('Y', 'N')) #confirming the levels in target variable | |
| loan_train$Loan_Status <- factor(loan_train$Loan_Status, levels = c('Y', 'N')) | |
| # Confirming the structure of the train data frame | |
| # Classification modelling | |
| # Logistic regression | |
| # Fit logistic regression model using all variables as predictors and Loan_Status as the response | |
| glm.fits <- glm(Loan_Status ~ Gender + Married + Dependents + Education + Self_Employed + ApplicantIncome + | |
| CoapplicantIncome + LoanAmount + Loan_Amount_Term + Credit_History + Property_Area, | |
| data = loan_train, | |
| family = binomial) | |
| # Summary of the model | |
| summary(glm.fits) | |
| # Coefficients of the model | |
| coef(glm.fits) | |
| # p-values of the coefficients | |
| summary(glm.fits)$coef[, 4] | |
| # Visual confirmation of loan status by Marital Status | |
| ggplot(loan_train, aes(x = Married, fill = factor(Loan_Status))) + | |
| geom_histogram(color = "red", alpha = 0.7, stat="count", bins = 30) + | |
| scale_fill_manual(values = c("Y" = "blue", "N" = "orange")) + # Using actual levels from Loan_Status | |
| labs(x = "Married", fill = "Loan Status") + | |
| ggtitle("Marital Status by Loan Status") + | |
| theme_bw() | |
| table(loan_train$Married, loan_train$Loan_Status) # [102, 62, | |
| # 238, 90] | |
| # I retrain the model using only the significant variables | |
| # Checking model fit on training data | |
| glm.fits_significant <- glm(Loan_Status ~ Married + Credit_History + Property_Area, | |
| data = loan_train, | |
| family = binomial) | |
| # Summary of the updated model | |
| summary(glm.fits_significant) | |
| # Predict probabilities for the model with significant variables | |
| glm.probs_significant <- predict(glm.fits_significant, type = "response") | |
| # Convert probabilities to class predictions (using 0.5 threshold) | |
| glm.pred_significant <- ifelse(glm.probs_significant > 0.5, "Y", "N") | |
| # Convert predictions and actual Loan_Status to factors | |
| glm.pred_significant <- factor(glm.pred_significant, levels = c("Y", "N")) | |
| loan_train$Loan_Status <- factor(loan_train$Loan_Status, levels = c("Y", "N")) | |
| # Confusion matrix using caret package for the model with significant variables | |
| conf_matrix_significant <- confusionMatrix(glm.pred_significant, loan_train$Loan_Status) | |
| # Print confusion matrix and performance metrics | |
| print(conf_matrix_significant) | |
| # Test data model fitting | |
| # Predict probabilities on the test set using the model with significant variables | |
| glm.probs_significant_test <- predict(glm.fits_significant, newdata = loan_test, type = "response") | |
| # Convert probabilities to class predictions (using 0.5 threshold) on the test set | |
| glm.pred_significant_test <- ifelse(glm.probs_significant_test > 0.5, "Y", "N") | |
| # Convert predictions and actual Loan_Status to factors for comparison | |
| glm.pred_significant_test <- factor(glm.pred_significant_test, levels = c("Y", "N")) | |
| loan_test$Loan_Status <- factor(loan_test$Loan_Status, levels = c("Y", "N")) | |
| # Confusion matrix using caret package for the test data | |
| conf_matrix_significant_test <- confusionMatrix(glm.pred_significant_test, loan_test$Loan_Status) | |
| # Print confusion matrix and performance metrics for the test set | |
| print(conf_matrix_significant_test) | |
| # ROC Curve | |
| # Load necessary libraries | |
| library(pROC) # For AUC and ROC calculations | |
| library(ggplot2) # For plotting | |
| # Predict probabilities on the test set using the model with significant variables | |
| glm.probs_significant_test <- predict(glm.fits_significant, newdata = loan_test, type = "response") | |
| # Create ROC object | |
| roc_obj <- roc(loan_test$Loan_Status, glm.probs_significant_test, levels = c("Y", "N")) | |
| # Print AUC value | |
| auc_value <- auc(roc_obj) | |
| print(paste("AUC:", auc_value)) | |
| # Plot the ROC curve | |
| ggroc(roc_obj) + | |
| ggtitle(paste("ROC Curve (AUC =", round(auc_value, 2), ")")) + | |
| theme_bw() | |
| # Linear Discriminant Analysis | |
| # Load necessary packages | |
| library(MASS) # For LDA | |
| library(caret) # For confusionMatrix | |
| # In LDA and QDA only numerical variables can be used as a common covariance is assumed by LDA. | |
| # Extracting numeric columns from loan_train | |
| numeric_cols_train <- sapply(loan_train, is.numeric) | |
| train_numeric <- loan_train[, numeric_cols_train] | |
| # Extracting numeric columns from loan_test | |
| numeric_cols_test <- sapply(loan_test, is.numeric) | |
| test_numeric <- loan_test[, numeric_cols_test] | |
| # Checking the structure of the extracted numeric columns | |
| str(train_numeric) | |
| str(test_numeric) | |
| # Add Loan_Status to the numeric data | |
| train_numeric$Loan_Status <- loan_train$Loan_Status | |
| test_numeric$Loan_Status <- loan_test$Loan_Status | |
| # Now, fit the LDA model on training data using the numeric columns | |
| lda_model <- lda(Loan_Status ~ ., data = train_numeric) | |
| summary(lda_model) | |
| # Predict on the test data using numeric columns | |
| pred_lda <- predict(lda_model, test_numeric)$class | |
| # Create a confusion matrix (predictions first, actuals second) | |
| conf_matrix_lda <- confusionMatrix(pred_lda, test_numeric$Loan_Status) | |
| # Print the confusion matrix and performance metrics for LDA | |
| print(conf_matrix_lda) | |
| # Quadratic discriminant Analysis | |
| # Load necessary packages | |
| library(MASS) # For QDA | |
| library(caret) # For confusionMatrix | |
| # Fit QDA model on training data using numeric columns | |
| qda_model <- qda(Loan_Status ~ ., data = train_numeric) | |
| summary(qda_model) | |
| # Predict on the test data using numeric columns | |
| pred_qda <- predict(qda_model, test_numeric)$class | |
| # Create a confusion matrix (predictions first, actual observations second) | |
| conf_matrix_qda <- confusionMatrix(pred_qda, test_numeric$Loan_Status) | |
| # Print the confusion matrix and performance metrics for QDA | |
| print(conf_matrix_qda) | |
| # Tree Based modelling | |
| # Classification Tree ( model using rpart) | |
| tree <- rpart(Loan_Status ~ ., data = loan_train, method = "class") | |
| rpart.plot(tree, nn = TRUE) | |
| print(tree) | |
| summary(tree) | |
| # Best Complexity Parameter (Pruning the tree) | |
| cp.optim <- tree$cptable[which.min(tree$cptable[,"xerror"]),"CP"] | |
| tree.pruned <- prune(tree, cp = cp.optim) | |
| rpart.plot(tree.pruned, nn = TRUE) | |
| summary(tree.pruned) | |
| print(tree.pruned) | |
| # Testing the model with Pruned Tree | |
| pred_tree <- predict(object = tree.pruned, loan_test, type = "class") | |
| conf_matrix_tree <- confusionMatrix(table(loan_test$Loan_Status, pred_tree)) | |
| print(conf_matrix_tree) | |
| # Bagging and Random Forests | |
| library(randomForest) | |
| ncol_train <- ncol(loan_train) - 1 | |
| print(ncol_train) # 11 variables excepting the target variable Loan_Status. | |
| # Bagging: Random Forest with mtry = total number of predictors | |
| set.seed(1987) | |
| bag.loan <- randomForest(Loan_Status ~ ., data = loan_train, mtry = 11, importance = TRUE) | |
| # Print the bagging model details | |
| print(bag.loan) | |
| varImpPlot(bag.loan, main = "Variable Importance plot of bagging Tree model") | |
| summary(bag.loan) | |
| # Predict on the test set using Bagging model | |
| bag_pred <- predict(bag.loan, newdata = loan_test) | |
| # Confusion matrix for Bagging model predictions | |
| conf_matrix_bag <- confusionMatrix(bag_pred, loan_test$Loan_Status) | |
| print(conf_matrix_bag) | |
| # Random Forest: Random Forest with mtry = subset of predictors (p/3 is default but | |
| # shall use approximation of sqrt(p) that is near sqrt(11) which is 4) | |
| set.seed(314) | |
| rf.loan <- randomForest(Loan_Status ~ ., data = loan_train, mtry = 4, importance = TRUE) | |
| # Print the random forest model details | |
| print(rf.loan) | |
| varImpPlot(rf.loan, main = "Variable Importance plot of Random Tree model") | |
| summary(rf.loan) | |
| # Predict on the test set using Random Forest model | |
| rf_pred <- predict(rf.loan, newdata = loan_test) | |
| # Confusion matrix for Random Forest model predictions | |
| conf_matrix_rf <- confusionMatrix(rf_pred, loan_test$Loan_Status) | |
| print(conf_matrix_rf) | |
| # Boosting | |
| # Load necessary libraries | |
| # Load necessary libraries | |
| install.packages("xgboost") | |
| install.packages("caret") | |
| library(xgboost) | |
| library(caret) | |
| # Create new data sets loan_train1 and loan_test1 to avoid overwriting original data sets | |
| loan_train1 <- loan_train | |
| loan_test1 <- loan_test | |
| # Convert Loan_Status to a numeric binary (0 = N, 1 = Y) in the new data sets | |
| loan_train1$Loan_Status <- ifelse(loan_train1$Loan_Status == "Y", 1, 0) | |
| loan_test1$Loan_Status <- ifelse(loan_test1$Loan_Status == "Y", 1, 0) | |
| # Convert categorical variables to dummy variables using model.matrix() | |
| # Remove the intercept column generated by model.matrix() with `[, -1]` | |
| train_matrix <- model.matrix(Loan_Status ~ . - 1, data = loan_train1) | |
| test_matrix <- model.matrix(Loan_Status ~ . - 1, data = loan_test1) | |
| # Check the resulting train_matrix and test_matrix | |
| str(train_matrix) | |
| str(test_matrix) | |
| # Convert data to D Matrix format for xgboost | |
| dtrain <- xgb.DMatrix(data = train_matrix, label = train_label) | |
| dtest <- xgb.DMatrix(data = test_matrix, label = test_label) | |
| # Set parameters for xgboost (for binary classification) | |
| params <- list( | |
| objective = "binary:logistic", # For binary classification | |
| eval_metric = "error", # Use classification error as the evaluation metric | |
| max_depth = 4, # Maximum depth of trees | |
| eta = 0.1, # Learning rate (shrinkage) | |
| nthread = 2 # Number of threads for parallel computing | |
| ) | |
| # Train the xgboost model | |
| set.seed(234) | |
| xgb_model <- xgboost( | |
| data = dtrain, | |
| params = params, # Parameters are provided here | |
| nrounds = 100, # Number of boosting rounds (trees) | |
| verbose = 0 # Turn off printing of boosting iterations | |
| ) | |
| summary(xgb_model) | |
| # Predict on the test data | |
| xgb_pred_prob <- predict(xgb_model, dtest) | |
| # Convert predicted probabilities to binary class predictions using 0.5 as threshold | |
| xgb_pred <- ifelse(xgb_pred_prob > 0.5, 1, 0) | |
| # Confusion matrix using caret package (reconverting numeric predictions back to factors for evaluation) | |
| xgb_pred_factor <- factor(xgb_pred, levels = c(0, 1), labels = c("Y", "N")) | |
| test_label_factor <- factor(test_label, levels = c(0, 1), labels = c("Y", "N")) | |
| # Print confusion matrix and performance metrics | |
| conf_matrix_xgb <- confusionMatrix(xgb_pred_factor, test_label_factor) | |
| print(conf_matrix_xgb) | |
| # Advanced EDA using PCA and Clustering | |
| # Creating a Data frame with only numerical variables | |
| # Identify the numeric columns in the loan final data frame | |
| numeric_cols_final <- sapply(loanfinal, is.numeric) | |
| # Extract only the numeric columns into a new data frame | |
| final_numeric <- loanfinal[, numeric_cols_final] | |
| # View the first few rows of the numeric data frame | |
| head(final_numeric) | |
| # Implementing a Principal Component Analysis Model | |
| names(final_numeric) | |
| apply(final_numeric, 2, mean) | |
| apply(final_numeric, 2, var) | |
| pr.out=prcomp(final_numeric, scale=TRUE) | |
| names(pr.out) | |
| print(pr.out) | |
| summary(pr.out) | |
| par(mfrow = c(1, 1)) | |
| plot(summary(pr.out)$importance[3,], ylab = "Cumulative Proportion of Variance Explained", | |
| xlab = "PC1 PC2 PC3 ", col= "red",pch= c(21, 22, 23, 24), cex = c(1,2,3,3), type = "b", bg = "yellow") | |
| title(main = "Cumulative Proportion of Variance Explained by the 3 Principal Components") | |
| pr.out$rotation=-pr.out$rotation | |
| pr.out$x=-pr.out$x | |
| biplot(pr.out, scale=0) | |
| pr.out$sdev | |
| pr.var=pr.out$sdev^2 | |
| pr.var | |
| pve=pr.var/sum(pr.var) | |
| pve | |
| par(mfrow = c(1, 2)) | |
| plot(pve, xlab="Principal Component", ylab="Proportion of Variance Explained", ylim=c(0,1), col= "purple",pch= c(21, 22, 23, 24), cex = c(1,2,3,3), type = "b", bg = "orange") | |
| plot(cumsum(pve), xlab="Principal Component", ylab="Cumulative Proportion of Variance Explained", ylim=c(0,1),col= "red",pch= c(21, 22, 23, 24), cex = c(1,2,3,3), type = "b", bg = "blue") | |
| # Hierarchical Clustering | |
| # Checking Correlation | |
| cor_matrix <- cor(final_numeric) | |
| library(ggcorrplot) | |
| ggcorrplot(cor_matrix, lab = TRUE) | |
| # Hierarchical clustering on different linkage methods | |
| hc.complete <- hclust(dist(final_numeric), method = "complete") | |
| hc.average <- hclust(dist(final_numeric), method = "average") | |
| hc.single <- hclust(dist(final_numeric), method = "single") | |
| # Set up a plotting area with 3 columns for subplots | |
| par(mfrow = c(1, 3)) | |
| # Plot the dendrograms for different linkage methods | |
| plot(hc.complete, main = "Complete Linkage", xlab = "", sub = "", cex = .9) | |
| plot(hc.average, main = "Average Linkage", xlab = "", sub = "", cex = .9) | |
| plot(hc.single, main = "Single Linkage", xlab = "", sub = "", cex = .9) | |
| # Combining Hierarchical Clustering with PCA | |
| hc.out <- hclust(dist(pr.out$x[, 1:3])) | |
| plot(hc.out, main = "Hierarchical Clustering on Three Principal Components", xlab = "Observations") | |
| clusters <- cutree(hc.out,2 ) | |
| table(clusters, loanfinal$Loan_Status) # clusters N Y 1 188 412 | |
| # 2 4 10 | |
| #SVM | |
| # Load necessary libraries | |
| library(e1071) | |
| library(ROCR) | |
| library(caret) | |
| library(caTools) | |
| library(smotefamily) | |
| # Apply SMOTE to balance the training data | |
| set.seed(123) # For reproducibility | |
| train_numeric_smote <- SMOTE(train_numeric[, -ncol(train_numeric)], # Exclude the target variable for SMOTE | |
| train_numeric$Loan_Status, # Target variable | |
| K = 5) | |
| # The SMOTE function from smotefamily package returns a list with 'data' that includes both features and the class | |
| train_smote <- train_numeric_smote$data | |
| # Ensure Loan_Status is a factor in the new dataset | |
| train_smote$Loan_Status <- as.factor(train_smote$class) | |
| # Drop the extra 'class' column (which is just a copy of Loan_Status) | |
| train_smote$class <- NULL | |
| # Check class distribution after SMOTE | |
| table(train_smote$Loan_Status) | |
| # Train an SVM model using the SMOTE-balanced data | |
| svmfit_smote <- svm(Loan_Status ~ ., data = train_smote, kernel = "radial", cost = 100, gamma = 4) | |
| summary(svmfit_smote) | |
| tune.smote.svm <- tune(svm, Loan_Status ~ ., data = train_smote, kernel = "radial", | |
| ranges = list(cost = c(0.1, 1, 10, 100, 1000), | |
| gamma = c(0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4))) | |
| summary(tune.smote.svm) | |
| # Tuned SVM modelwith best parameters | |
| svmfit_smote <- tune.smote.svm$best.model # since accuracy is low this may be due to overfitting | |
| # I shall try hyper parameter tuning | |
| # Ensure that Loan_Status in test_numeric is a factor | |
| test_numeric$Loan_Status <- as.factor(test_numeric$Loan_Status) | |
| # Use the trained SVM model (svmfit_smote) to make predictions on the test set | |
| ypred_test <- predict(svmfit_smote, test_numeric) | |
| # Create a confusion matrix to evaluate the predictions | |
| confusion_matrix_test <- table(Predicted = ypred_test, Actual = test_numeric$Loan_Status) | |
| print(confusion_matrix_test) | |
| # If you want to compute other metrics like accuracy, precision, recall, etc., you can use the caret package | |
| library(caret) | |
| # Compute confusion matrix and other performance metrics | |
| conf_matrix_svm <- confusionMatrix(ypred_test, test_numeric$Loan_Status) | |
| # Print the confusion matrix and performance metrics | |
| print(conf_matrix_svm) | |
| # Visualizing SVM on PCA | |
| # Load necessary libraries | |
| library(e1071) | |
| library(ggplot2) | |
| library(caret) # For evaluation metrics like confusion matrix | |
| # Step 1: Apply PCA on the training data (excluding the target variable) | |
| pca_model <- prcomp(train_smote[, -ncol(train_smote)], center = TRUE, scale. = TRUE) | |
| # Extract the first two principal components from the training data | |
| train_pca <- data.frame(PC1 = pca_model$x[, 1], PC2 = pca_model$x[, 2], Loan_Status = train_smote$Loan_Status) | |
| # Step 2: Tune SVM model on the PCA-transformed training data | |
| set.seed(123) # For reproducibility | |
| tune.out <- tune(svm, Loan_Status ~ ., data = train_pca, kernel = "radial", | |
| ranges = list(cost = c(0.1, 1, 10, 100), | |
| gamma = c(0.01, 0.1, 0.5, 1))) | |
| # Get the best model from the tuning process | |
| best_model <- tune.out$best.model | |
| # Step 3: Apply PCA on the test set (transform test data using the same PCA model) | |
| test_pca <- data.frame(PC1 = predict(pca_model, test_numeric[, -ncol(test_numeric)])[, 1], | |
| PC2 = predict(pca_model, test_numeric[, -ncol(test_numeric)])[, 2], | |
| Loan_Status = test_numeric$Loan_Status) | |
| # Step 4: Test the best model on the PCA-transformed test data | |
| pred_test <- predict(best_model, test_pca) | |
| # Confusion matrix to evaluate performance on the test set | |
| confusion_matrix_test <- confusionMatrix(pred_test, test_pca$Loan_Status) | |
| print(confusion_matrix_test) | |
| # Step 5: Plot the decision boundary using the best model | |
| # Create a grid of points for decision boundary visualization | |
| x_min <- min(train_pca$PC1) - 1 | |
| x_max <- max(train_pca$PC1) + 1 | |
| y_min <- min(train_pca$PC2) - 1 | |
| y_max <- max(train_pca$PC2) + 1 | |
| # Create a grid of values | |
| grid <- expand.grid(PC1 = seq(x_min, x_max, length.out = 200), | |
| PC2 = seq(y_min, y_max, length.out = 200)) | |
| # Predict on the grid using the best model | |
| grid$Loan_Status <- predict(best_model, grid) | |
| grid$Loan_Status <- as.numeric(grid$Loan_Status) # Convert factor to numeric | |
| # Step 6: Plot the decision boundary | |
| ggplot() + | |
| geom_point(data = train_pca, aes(x = PC1, y = PC2, color = Loan_Status), size = 2) + | |
| geom_tile(data = grid, aes(x = PC1, y = PC2, fill = Loan_Status), alpha = 0.3) + # Better visualization | |
| labs(title = "SVM Decision Boundary on PCA-Transformed Data", | |
| x = "Principal Component 1", | |
| y = "Principal Component 2") + | |
| theme_minimal() + | |
| scale_color_manual(values = c("blue", "red")) + | |
| scale_fill_gradient(low = "lightblue", high = "yellow") | |
| # Print out the best parameters found during tuning | |
| print(tune.out$best.parameters) | |
| # Comparison of all the models | |
| # Create a function to extract metrics from a confusion matrix | |
| extract_metrics <- function(conf_matrix) { | |
| accuracy <- conf_matrix$overall['Accuracy'] | |
| sensitivity <- conf_matrix$byClass['Sensitivity'] | |
| specificity <- conf_matrix$byClass['Specificity'] | |
| positive_predictive_value <- conf_matrix$byClass['Pos Pred Value'] # Precision | |
| return(c(accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive_predictive_value)) | |
| } | |
| # Extracting metrics for each model | |
| metrics_logistic <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_significant_test) | |
| metrics_lda <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_lda) | |
| metrics_qda <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_qda) | |
| metrics_tree <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_tree) | |
| metrics_bagging <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_bag) | |
| metrics_rf <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_rf) | |
| metrics_xgb <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_xgb) | |
| metrics_svm <- extract_metrics(conf_matrix_svm) | |
| # Combine all metrics into a data frame | |
| model_comparison <- data.frame( | |
| Model = c("Logistic Regression", "LDA", "QDA", "Decision Tree", "Bagging", "Random Forest", "XGBoost", "SVM"), | |
| Accuracy = c(metrics_logistic[1], metrics_lda[1], metrics_qda[1], metrics_tree[1], metrics_bagging[1], metrics_rf[1], metrics_xgb[1],metrics_svm[1] ), | |
| Sensitivity = c(metrics_logistic[2], metrics_lda[2], metrics_qda[2], metrics_tree[2], metrics_bagging[2], metrics_rf[2], metrics_xgb[2], metrics_svm[2]), | |
| Specificity = c(metrics_logistic[3], metrics_lda[3], metrics_qda[3], metrics_tree[3], metrics_bagging[3], metrics_rf[3], metrics_xgb[3], metrics_svm[3]), | |
| Positive_Predictive_Value = c(metrics_logistic[4], metrics_lda[4], metrics_qda[4], metrics_tree[4], metrics_bagging[4], metrics_rf[4], metrics_xgb[4], metrics_svm[4]) | |
| ) | |
| # Rank models by Accuracy | |
| model_comparison <- model_comparison[order(-model_comparison$Accuracy), ] | |
| # Display the results | |
| print(model_comparison) | |
| # This completes the Project |



© 2025 Syed Faizan. All Rights Reserved.